Research Finds Loud Noises Can Lead to Fluid Buildup in the Ear
According to the World Health Organization, over 1 billion young adults are at risk of permanent, avoidable hearing loss due to unsafe listening practices. This includes listening through headphones at a high volume for prolonged amounts of time and attending concerts and sporting events at Hertz Arena without wearing hearing protection.
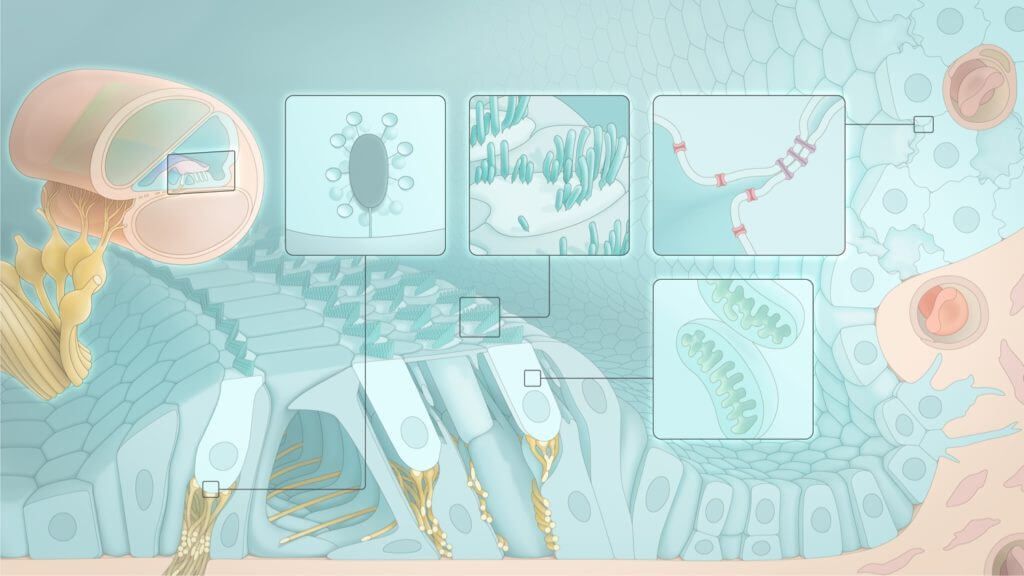
While it’s well established that loud sounds cause hearing loss, the mechanism behind this phenomenon was not well understood. Recent research has uncovered that loud noises can actually lead to fluid buildup in the ear, contributing to hearing loss.
About the Study
The study, entitled “Endolymphatic Hydrops Is a Marker of Synaptopathy Following Traumatic Noise Exposure,” was published in the journal Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology in November of 2021. The research team includes students at the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California.
They found that loud sounds not only cause a loss of auditory nerve cells in the inner ear, but also that exposure to them is associated with a condition known as endolymphatic hydrops, which is a buildup of fluid in the inner ear.
Additionally, they uncovered that treating this fluid buildup with a saline solution lessened nerve damage.
Study Implications
Loss of nerve cells in the inner ear is sometimes known as “hidden hearing loss” since tests often cannot detect the damage. However, scanning for fluid buildup can help experts diagnose impending nerve damage and take steps to prevent it.
According to lead study author John Oghalai, M.D., “First, if human ears exposed to loud noise, such as a siren or airbag deployment, can be scanned for a level of fluid buildup – and this technology is already being tested out – medical professionals may have a way of diagnosing impending nerve damage. Secondly, if the scan discovered fluid buildup, people could be treated with hypertonic saline and possibly save their hearing.”
In addition, this research has important implications for the research and treatment of Meniere’s disease, a condition that causes episodes of hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ear) and vertigo (spinning sensation) that is thought to be caused by a buildup of fluid in the ear.
For more information or to schedule an appointment for a hearing test, call Center For Hearing today.
- Understanding Infant Hearing Loss
- The Relationship Between Exercise and Hearing Loss
- Muffled Hearing: Common Causes and Solutions